Planning to buy a home ? One must know about RERA Act
Introduction of RERA Act, 2016
Real Estate Regulatory Authority Act, 2016 is an act by the parliament of India. Also, the act was introduced to safeguard home-buyers and moreover, it assist in amplifying the investments in the real estate industry. The act was introduced by the Rajya Sabha and Lok Sabha. The act was commenced on 1st may 2016 linking 59 to 92 sections broadcast. The state and central government are responsible for alerting about the rules under the RERA Act within directive time six months of period. The RERA License is mandatory for the homebuyers.
Features of the RERA act
RERA act institutes to intensify liability and clarity with respect to housing purchases and real estate. The impact of RERA on homebuyers is commendable as they can invest freely with confidence.
Now, Let us look at the key features of RERA Act.
- Demonstration of RERA in every Indian state with the power to control, observe, watch, settle and reconcile any conflicts with honor to real estate plans in the preferred state.
- In accordance with the current law, the real estate investor can’t execute any modifications to the project without the written permission of the customer buying home. This terms will not permit the real estate developer to boost the value price of their plans.
- Certification and registration are compulsory for all industrial and domestic real estate plans. In the case of the home, it is across 500 square metres either comprises 8 apartments or which are under development and construction.
- The prime feature of the RERA is the real estate developer will have to place 70% of the money received from the real estate buyer in a separate security account. To reach the building price value of the project plan. This will hold an inspection on a real estate investor who distracts the buyer’s cash to commence a fresh project. Alternately of finishing the money that was collected and in order for securing the particular project is finished in time.
- Leaving and declining the registration a property will drag a penalty up to 10% of the project plan price value. Repeated mistakes by the real estate developer could send them in jail.
Functioning of Rera Act
- The act institutes to the real estate regulatory and authority for promotion and guiding the real estate sector. The act also fortifies sale of apartment, plot, and sale of real estate subjects in an effective and visible way.
- The RERA Act engrosses the customers in the sector and also initiate a resolving system for sharp modifications.
- The RERA Act demonstrate the authority for appeals courts to listen to the appeals from the conclusions and administers the orders of RERA.
The Govt of India Ministry of Housing& Urban Affairs notify all about the RERA ACT and the orders.
Rules of RERA Act
The act, 2016 under Section 84 intends within a period of six months from its initiation date and state governments will establish the rules to follow up with the plans associated with the Act. The registration project under RERA has a set of rules and regulations that are obligatory to follow.
- Within 6 months of the RERA Act being imposed the state Governments should make rules for conducting the terms and outlines of the Act. The spoken rules caution by the particular state government. The ministry of housing & Urban population notifies the central government to issue the real estate rules for regulation and development in general. The rules direct in 2016 on October 31st. The Rules circulated by the central government are appropriate to Andaman & Nicobar Islands, Dadra & Nagar Haveli, Daman & Diu, Lakshadweep, Chandigarh and many more. The rules declare after the previous statement of a sketch for remarks.
- In the RERA act, Real Estate Developer requires to invest 70% of the money received from buyers in a separate bank account generated for the project’s plans. They require to manage this money deposit only for the development of the project’s plans. They need to engross the duration for the fulfillment of the projects. Any difference in this would drag penalty plus imprisonment.
List of states initiated RERA act
[fusion_table fusion_table_type=”2″ hide_on_mobile=”small-visibility,medium-visibility,large-visibility” class=”” id=”” animation_type=”” animation_direction=”left” animation_speed=”0.3″ animation_offset=””]
| States | Date | Month | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| Uttar Pradesh | 11 | October | 2016 |
| Gujarat | 20 | October | 2016 |
| Madhya Pradesh | 22 | October | 2016 |
| Lakshadweep | 31 | October | 2016 |
| Chandigarh | 31 | October | 2016 |
| Daman & Diu | 31 | October | 2016 |
| Dadra & Nagar Haveli | 31 | October | 2016 |
| Andaman & Nicobar Island | 31 | October | 2016 |
| Delhi | 24 | November | 2016 |
| Odisha | 25 | February | 2017 |
| Andhra Pradesh | 28 | March | 2017 |
| Maharashtra | 19 | April | 2017 |
| Chattisgarh | 26 | April | 2017 |
| Uttrakhand | 28 | April | 2017 |
| Bihar | 1 | May | 2017 |
| Rajasthan | 1 | May | 2017 |
| Jharkhand | 18 | May | 2017 |
| Punjab | 8 | June | 2017 |
| Tamil Nadu | 22 | June | 2017 |
| Karnataka | 10 | July | 2017 |
| Haryana | 28 | July | 2017 |
| Telangana | 4 | August | 2017 |
| Himachal Pradesh | 28 | September | 2017 |
| Goa | 24 | November | 2017 |
[/fusion_table]
The table shows that at what date, month and year the states initiated the RERA act and protects home buyers. It aims for promotion and progression of the regularity of systems and actions in the real estate sector.
How the RERA Act serves the best to home buyers?
The RERA act has numerous perks for the promoter, the real estate agent and the buyers. This how the RERA benefits the homebuyers and can serve you best :
- If there is a conflict in terms of what guarantees by the builder and what delivers. The home buyer authorizes to receive a full amount refund that was given as advance. Sometimes the developer may provide interest on the cost as well.
- The buyer has the perfect right to information regarding the project plans. This includes plans related to purpose, achievement, and finish status.
- Before getting Rera license, the builder assumes the cost of a project plan and never provide full-fledged information. But, in order to get a RERA license, currently, a regular method is being adapted to estimate the carpet area. Moreover, the promoters cannot present fill carpet areas to boost costs.
- In 5 years of ownership, if there is any architectural flaws or obstacles in the essence of quality. The builder has to reform these losses in 30 days at no charge to The prime feature of the RERA is the real estate developer will have to place 70% of the money received from a buyer in a separate security account. To reach the building price value of the project plan. This will hold an inspection on a real estate investor who distracts the buyer’s cash to commence a fresh project. Alternately of finishing the money that was collected and securing the particular project is finished in time the purchaser buy it.
- In accordance with rules and regulation of RERA, a developer cannot take any extra than 10% of the charge of the project plans from the purchaser as advance fees. This protects the purchaser from having to source funds quick and ought to spend a huge cost.
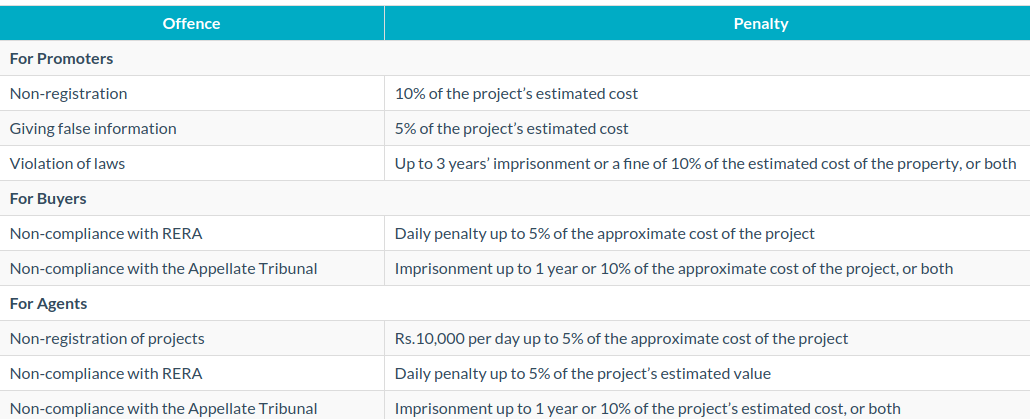
Penalties Under RERA
If you decline to match all of RERA’s rules, the resulting penalties will be suitable.
The RERA Act determines to provide the Indian real estate commerce with its primary regulator. The Real Estate Act gives it obligatory for every state to develop its individual control. Even to outline the precepts that will supervise the operations of the regulator.
If you are planning to buy a home you may cater to RERA services. For more details about RERA Act visit our website Legal Raasta and for more information regarding RERA License. Our expert will guide you best for the registration process and buying and selling of the company. For any query mail us on contact@legalraasta.com or you can ring at 8750008585 to get more services from us.
Related articles