How can UAN helpdesk serves you ?
What is UAN Helpdesk?
UAN helpdesk is helpdesk that you can connect with the source of the internet that is online contact administration accessible on the EPFO helpdesk login the governmental website that delivers all the services connected with EPF registration for the employees and employers. The genuine question always raised by the employee or the people is that. How can we connect for EPF details? What is a source of connecting to the Helpdesk? Here is the contact number for UAN helpdesk 1800 118 005 you can call on this number for any details related to EPF and for any complaints. Employees and employers can call on the UAN helpdesk number in working hours of company, firms or business for helping with Employee provident fund matters or subject of issues.
What is UAN?
The UAN called Universal Account Number. It is a 12-digit character given by EPFO (Employee Provident Fund Organization) and assigns to EPF members ( Employee Provident Fund). The EPFO provide him/her power to operate the EPF account and reduces the part of the employer. Member License Characters or Member Id is the number provided by EPFO to authorize the employer to offer EPF money of employee. When the employee shifts the job then the fresh employer will start a fresh account number for its employee in EPFO. Therefore, a fresh Member ID will be assigned to the employee. Member ID is related as Provident Fund number at the beginning. Hence, you would have several Member ID as the number of employers participating in your support to the Employee Provident Fund Organisation.
How will UAN help you?
A UAN will be originated for every provident fund provided to members by EPFO. The UNA will act as a sunshade for the several member Ids provided to the persons by a different business or firms. The idea is to combine several Member verification numbers or Ids given to a solo member under solo UAN. This will assist in reviewing the details of all the members’ verification number connected to it.
The ways in which UAN can help you in many ways as follows:
- There is no need for fund transfer as of the introduction of the UAN. Employee provident fund account from one employer account to another was a slow process. However, the UAN you don’t require to shift your funds in any situations. Only you need to provide your KYC, UAN information and details to a fresh employer. After the fresh employer confirms the details, the money from the earlier account gets a shift to the fresh account.
- Even there is no need for employees to involve in withdrawals. In this present time, the new terms and conditions are applicable. Every application for EPF withdrawal has to be approved by your earlier employer. After the approval, the application is forward to the Employee Provident Fund Organization. There would be no requirement for shifting applications. The cost value in your earlier account will automatically get a shift to your fresh account on basis of verifications.
- The UAN helps provides repeated SMS alerts every month. This will assist when your employer and you provide to your EPF account with details and by a message you will undergo warning signal from the EPFO.
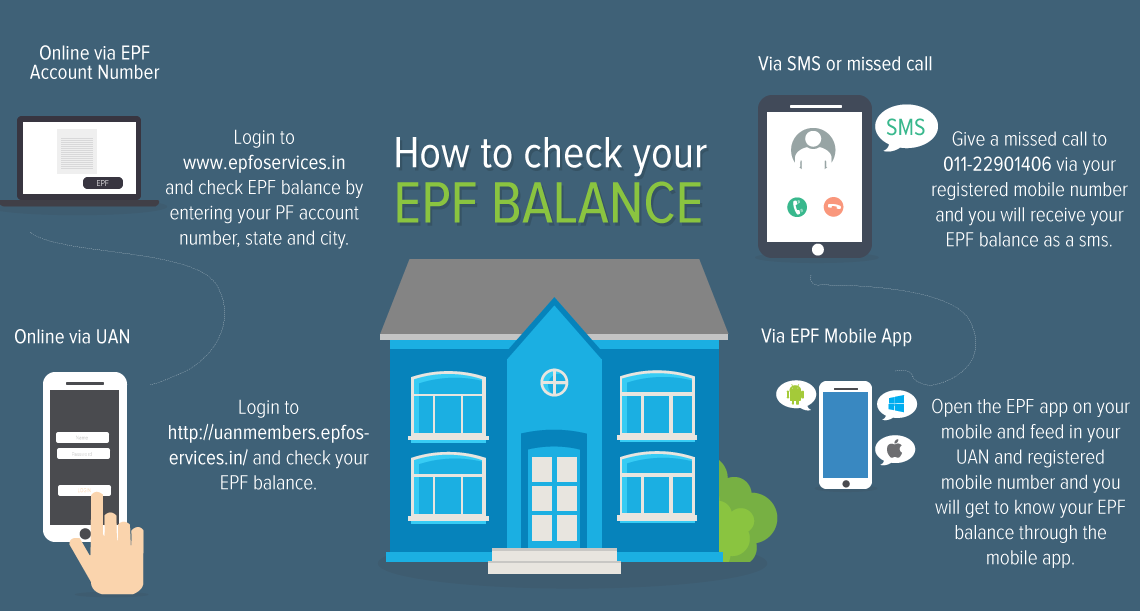
- The UAN checks all the related data to EPF. It can be UAN registration, Distribution of UAN and to check the balance of EPF online. Even you will cater the data about how can you grab your EPF amount from the non-functional account.
How will UAN helpdesk serve Employers or the employees?
The UAN helpdesk is always ready to serve all the employers and employees for there EPF account security and there is no issue of transferring.UAN Activation Online is the best way to cater to registration. It completely erases the work for members of EPF and all the credit goes to the EPFO. Let’s discuss a few of the formats of Helpdesk on which an employer or the employee can check the EPF balance or make complaints with help of UNA number.
-
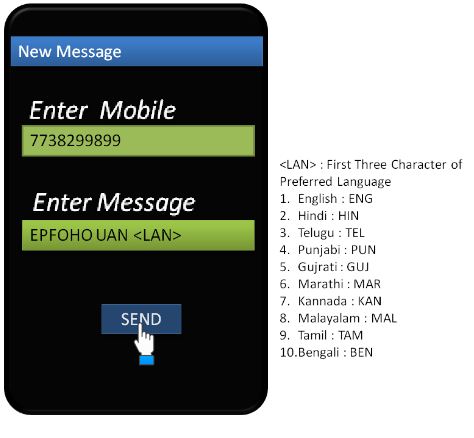
SMS service
For the benefit of the EPF members, the EPFO has originated SMS services to ease there work of checking the data of the EPF account. A person who has initiated UAN could use the messaging service to inspect data of his/her Provident fund account. The messaging format will be format is EPFOHO<UAN>LAN. when the message is ready to send SMS on this number 7738299899. LAN in the messaging format indicates language a regional language. This facility is accessible in 10 different main Indian languages including English and Hindi
-
Mobile Application (Play store or Apple store)
The Internet is key to the usage of a mobile application. The is Android version is ready to serve you in providing all kind of data. You can simply download the app of EPF. The EPF members could avail the Provident fund linked data by applying for the UAN number.
-
Centralized Public Grievance Redress and Monitoring System
CPGRAMS is an action took by the central government that authorizes and observes the complaint inscribed by any person. A Provident fund member can disclose his or her complaint on the CPGRAMS portal.
-
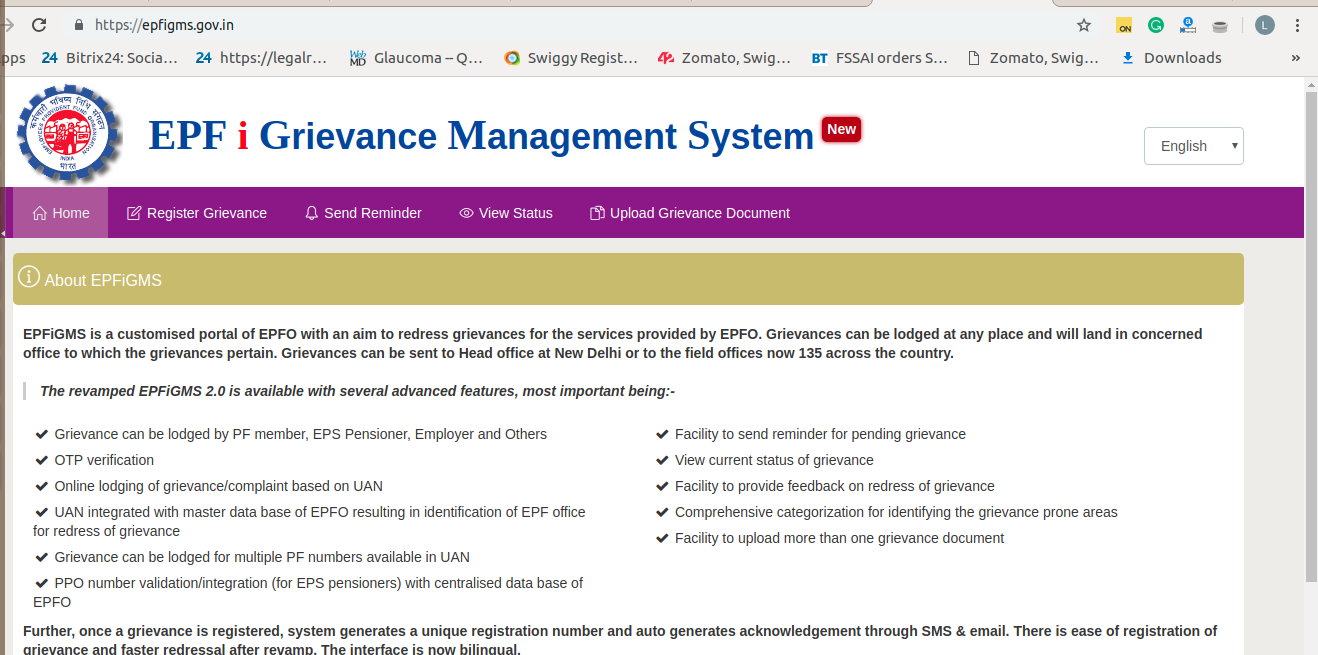
Employees’ Provident Fund (EPF) Online Grievance Management System
EPFiGMS is an online based complaint about damages system used by EPFO. This portal permits anybody to file his or her complaint in the system 24×7. As the complaint files, an unusual number will assign to the applicant. This unusual number supports him/her to hold a track of the situation of the complaint redressal. All complaint approaches will put under the strict monitoring of the EPFiGMS system on a regular basis at every level of standard surveillance.
-
Inoperative Account Helpdesk
For pursuing inoperative PF accounts, the person connected to EPF can reach the UAN helpdesk for inoperative accounts. Follow these referred guidelines by EPFO inoperative Account Help Desk.
All of the above services helps as UAN helpdesk for registering any issues or complaints connected to EPF just contact through these sources and look forward to registration or UAN number allotment.
For more details connected with EPF Registration and ESI Registration, you can have a look at our website services LegalRaasta.Even you can give us a call at 8750008585 and feel free to send your query on Email: contact@legalraasta.com
Related Article
FAQs on Online ESI Registration in India